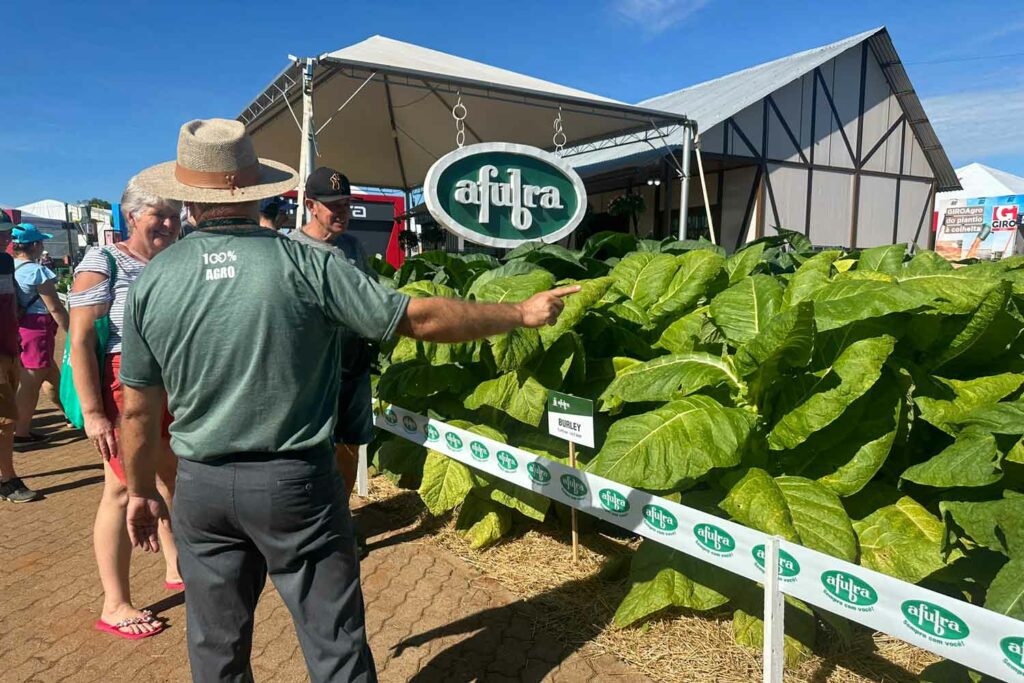
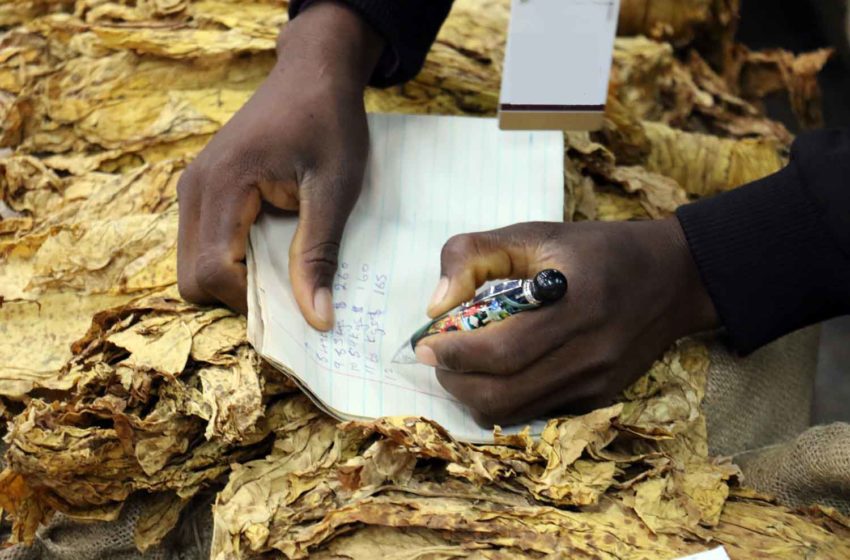
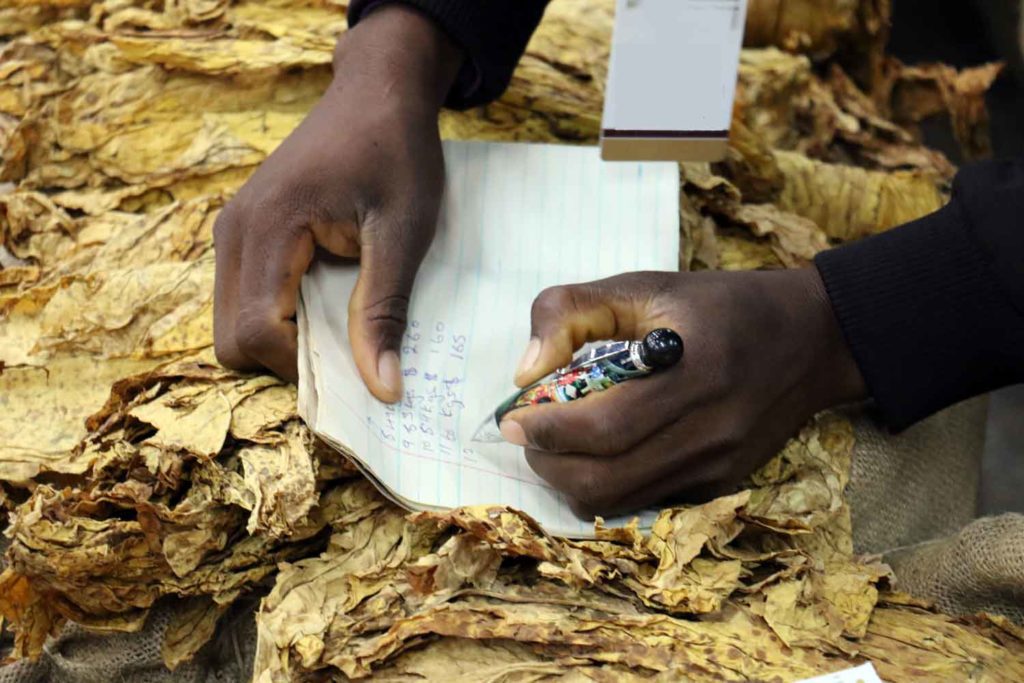
Stakeholders highlighted tobacco industry initiatives to preserve Brazil’s native forests and achieve energy self-sufficiency at the Expoagro Afubra 2024 fair in Rio Pardo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, on March 22.
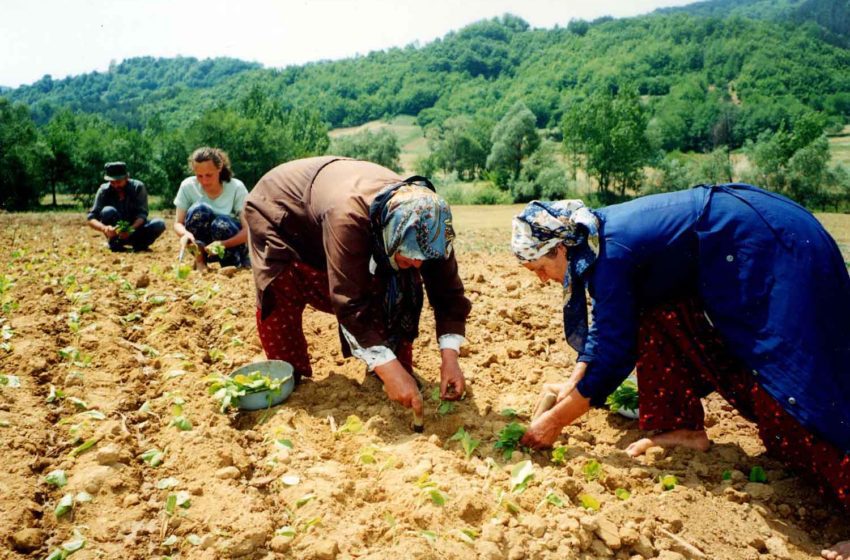
SindiTabaco technical advisor Fernanda Viana Bender presented a number of projects designed to promote forest sustainability in tobacco farming in partnership with the Federal University of Santa Maria (UFSM).
The program aims to cultivate trees to meet tobacco farmers’ fuel requirements while preserving native forests. At 22 demonstration units in Rio Grande do Sul, the UFSM research team, led by Jorge Antonio de Farias, is testing the management of fast-growing trees.
While the programs provide stakeholders with valuable knowledge, Bender says there is still much to learn. “We need to develop a way of thinking that forest production is a tobacco farmer’s business,” she was quoted as saying on SindiTabaco’s website. “Without wood, there is no tobacco curing. However, beyond the demand by the sector, farmers could also get organized to diversify with forest production, thus earning extra income,” she argued.
Farias identified a number of challenges to achieving those goals. “As the farmers possess small farms, land availability is one of the problems that make it difficult to plant trees, and the same holds true for the transport logistics of the production,” he observed.
“At the same time, we witness a sector extremely concerned with the supply of wood of legal origin while the farmers strongly demand wood. The solution goes through the creation of cooperatives or associations capable of articulating this market, and the tobacco sector could be a protagonist in this process. The forest component should become an integral part, when it comes to establishing a rural property, as an alternative source of income,” said Farias.







 22nd Century Group reported net revenues of $7.4 million for the quarter that ended Dec. 21, 2023, down from net revenues of $10 million in the comparable 2022 quarter. Gross loss for the fourth quarter was $7.8 million compared with a gross loss of $100,000 in the prior-year period. The loss included a one-time charge of $7.9 million for certain inventory write-down adjustments.
22nd Century Group reported net revenues of $7.4 million for the quarter that ended Dec. 21, 2023, down from net revenues of $10 million in the comparable 2022 quarter. Gross loss for the fourth quarter was $7.8 million compared with a gross loss of $100,000 in the prior-year period. The loss included a one-time charge of $7.9 million for certain inventory write-down adjustments.