What can we learn from the first FDA marketing order for menthol ENDS?
By Chris Allen
In good news for the next-generation nicotine industry, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently granted marketing orders (MOs) for four menthol-flavored e-cigarette products. This marks the first time that the FDA has granted MOs for nontobacco-flavored products via the premarket tobacco product application (PMTA) pathway. In this article, Chris Allen, CEO of PMTA specialist Broughton, summarizes the documentation and shares some pertinent learning points from the decision summaries of the applications from the technical project lead (TPL) review.
The new products that were granted MOs are Altria’s Njoy Ace Pod Menthol 2.4 percent, Njoy Ace Pod Menthol 5 percent, Njoy Daily Menthol 4.5 percent and Njoy Daily Extra Menthol 6 percent. The Ace products are sealed pod-based systems whereas the Daily products are disposable e-cigarettes with a prefilled, nonrefillable e-liquid reservoir. At the time of writing, Njoy Ace is the only pod-based e-cigarette product with an MO.
A Big Step for Tobacco Harm Reduction
Granting an MO for a menthol e-cigarette is a huge step in the right direction for the FDA, opening up a new avenue for tobacco harm reduction to millions of adult smokers across the U.S.
It is crucial that we have a diverse portfolio of convenient, satisfying and appealing smoke-free products to meet adult smokers’ preferences and needs as they transition away from combustible cigarettes (CC). We hope the fact that the FDA has granted MOs for menthol products will encourage adult smokers to opt for regulated alternatives to smoking rather than illicit products. However, we must bear in mind that these products are now eight years old, so it’s imperative that the FDA streamlines the PMTA process to reduce the time to market for products that are aligned with changing consumer behaviors.
The PMTA Process
Compiling a PMTA is a rigorous and lengthy task, with manufacturers required to provide data and evidence to demonstrate that the product is “appropriate for the protection of public health” (APPH) as required under the Tobacco Control Act. Manufacturers must consider the risks and benefits of the product, both to users and nonusers. To date, 27 products and devices have been granted marketing orders, and a full list is kept here.
The FDA’s approval of menthol products demonstrates that it is possible to achieve the requirements of PMTA approval with a high-quality menthol product and compelling data. Shannon Leistra, president and CEO of Njoy, said, “We believe these marketing orders are a testament to the quality of the Njoy products and the strength of evidence supporting the authorizations of the Njoy menthol e-vapor products.”
It will be interesting to see the FDA’s next move regarding flavored electronic nicotine-delivery systems (ENDS) and whether granting MOs for menthol opens up the door to other flavors. Njoy has resubmitted PMTAs for blueberry-flavored and watermelon-flavored pod products that work exclusively with the new Njoy Ace 2.0 age-gated device and is awaiting the outcomes.
What Can We Learn from These Products?
PMTAs are reviewed on a case-by-case basis, and the MO is specific to these products only. Understandably, many in the industry are looking to learn from this industry first to apply it to their own products and PMTAs.
The most interesting outcome, naturally, is that the FDA determined there was robust and reliable evidence of an added benefit from the menthol flavor relative to that of tobacco-flavored products in facilitating adult smokers switching from CCs. This was deemed to outweigh the increased risk of youth use.
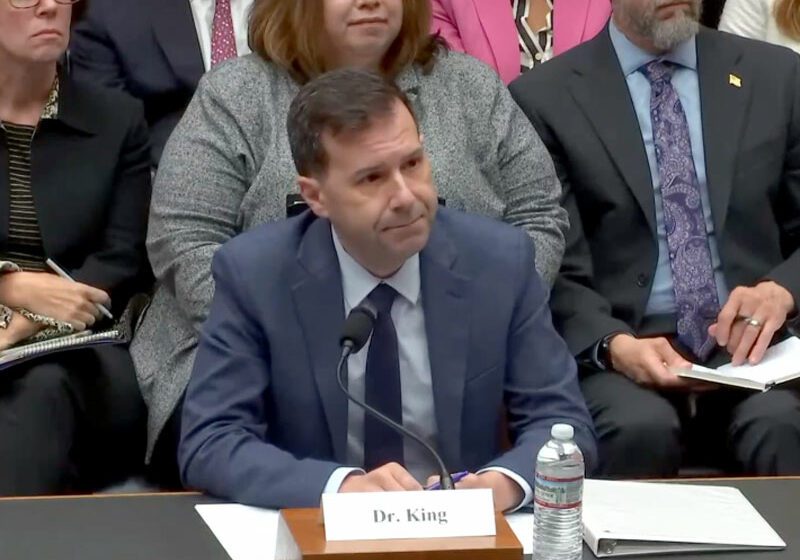
About the approval, Brian King, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products, said, “It is the responsibility of the applicant to provide the necessary evidence to obtain marketing authorization, and the FDA has made clear what’s needed to successfully achieve that outcome. This action is further reinforcement that authorization of an e-cigarette product is possible when sufficient scientific evidence has been submitted to the agency to justify it.”
Reducing the Risk of Youth Use
A shared concern of the general public, manufacturers and regulators is the youth appeal of nontobacco-flavored products. The FDA has placed stringent marketing restrictions to prevent youth access and exposure, and for flavored products, there is a higher burden of proof on the manufacturer that the benefit to adults who use CCs outweighs the increased risk of youth use.
While the application did include studies of youth use with low prevalence estimates for the new products, the FDA deemed the sample size insufficient. It noted the recent National Youth Tobacco Survey on popular flavors and devices, referencing the increased risk of youth appeal of menthol-flavored ENDS compared with tobacco-flavored ones, but adding the risk is lower than some other flavors (e.g., fruit).
The TPL noted, “FDA’s experience shows that advertising and promotion restrictions and sales access restrictions cannot mitigate the substantial risk to youth from flavored ENDS sufficiently to reduce the magnitude of adult benefit required to demonstrate APPH. Rather, for flavored ENDS, only the most stringent mitigation measures have such potential; to date, the only such measures identified with the potential for that kind of impact have been device access restrictions.”
The FDA’s ruling highlights that “stringent mitigation measures” such as device access restrictions have the mitigation potential to demonstrate APPH. However, the Njoy menthol-flavored PMTAs did not propose such mitigation restrictions and therefore required reliable and robust evidence of a potential benefit to adults who smoke, i.e., cessation of combustibles with continued ENDS use or cessation of combustibles leading to cessation of ENDS use.
The application also proposed limiting youth exposure by not engaging in social media promotions, limiting human portrayals to those over 45 and prohibiting these products from being sold on third-party websites.
Comparisons from Adult Smokers
In this case, the FDA found “acceptably strong evidence” from submitted data from an online, observational longitudinal cohort study comparing its menthol Njoy Daily product with its tobacco-flavored Njoy Daily device. The study suggested a 21 percent to 31 percent rate of switching over a period of six months (three months primary outcome cohort), higher than the rate of ENDS in the literature.
The comparison analyses showed the menthol Daily products were associated with statistically significant and higher rates (32 percent to 43 percent) of complete switching than the rate of tobacco-flavored Njoy Daily ENDS (21 percent to 37 percent) at three months or six months.
Additionally, the comparison analyses demonstrated a 24 percent to 45 percent substantial added benefit from the menthol-flavored Njoy Daily ENDS in switching away from CCs among smoking adults compared with their tobacco-flavored equivalent. The submitted clinical studies demonstrated a similar abuse liability to CCs, suggesting they are a suitable substitute.
For Njoy Ace menthol products, the longitudinal cohort study found behavioral benefits compared with tobacco-flavored Njoy Ace products in robust and reliable rates of switching from CCs, though the exact figures were redacted.
Overall, the studies showed that the products have the potential to promote CC cessation, or significantly reduced use, compared with tobacco-flavored comparator products. The review concluded that there was a benefit to public health in the significantly higher smoking cessation rates achieved as compared with equivalent tobacco-flavored products.
Biomarker data showed fewer and lower levels of harmful and potentially harmful constituent exposure compared with CCs, and toxicological evaluation of the aerosol suggested a lower excess lifetime cancer risk using Njoy Daily than using CCs. Ultimately, the FDA ruled that this data “demonstrated the potential for these new products to benefit adults who smoke combustible cigarettes as compared to adults who continue to use combustible cigarettes exclusively.”
All of these points contributed to the FDA’s decision to designate the products as APPH. This monumental ruling has excited many in the next-generation nicotine industry, as it helps us achieve our shared goal of tobacco harm reduction for millions of adult smokers across the U.S. We are likely to see manufacturers working closely with regulatory consultants like Broughton to ensure their PMTAs contain robust and rigorous data and that their regulatory dossier is presented to support the best chance of success.












 Accorto Regulatory Solutions has joined the Global Institute for Novel Nicotine (GINN), an organization dedicated to advancing tobacco harm reduction through supporting the research and development of non-vaporized tobacco alternatives for adult smokers. The GINN also promotes compliance standards, focusing on youth access prevention, responsible marketing and product quality.
Accorto Regulatory Solutions has joined the Global Institute for Novel Nicotine (GINN), an organization dedicated to advancing tobacco harm reduction through supporting the research and development of non-vaporized tobacco alternatives for adult smokers. The GINN also promotes compliance standards, focusing on youth access prevention, responsible marketing and product quality.