Knowledge-Action-Change (KAC) has published the latest in a series of briefing papers as part of its Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction (GSTHR) project.
What are nicotine pouches? provides an overview of the latest information about the scientific evidence, market data, regulatory landscape and tobacco harm potential for this relatively new safer nicotine product, according to KAC.
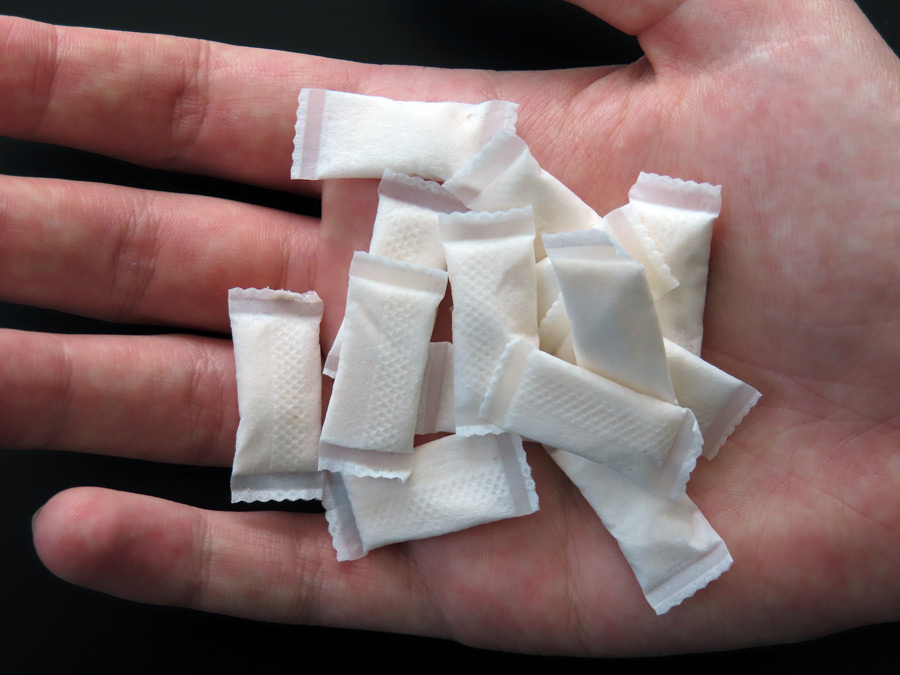
Nicotine pouches are thumbnail-sized sachets that are placed under the lip. They are made from vegetable fibers infused with nicotine and a range of flavors. Nicotine pouches are sometimes confused with Swedish snus, another safer nicotine product that was the subject of a previous GSTHR briefing paper. Both products are placed under the lip, but while Swedish snus contains tobacco, nicotine pouches do not contain any raw or processed tobacco leaves.
As a new product category, the body of evidence examining their safety is still growing, but preliminary findings indicate that nicotine pouches offer people who use nicotine a significantly safer alternative to smoking.
“This briefing paper aims to increase knowledge about, and awareness of, the tobacco harm reduction potential of nicotine pouches,” said Gerry Stimson, director of KAC and emeritus professor at Imperial College London. “Good quality information about the full range of different safer nicotine products is essential for consumers, policymakers and regulators.
“Nicotine pouches could make a significant contribution to tobacco harm reduction. This is particularly the case for the more than 300 million people worldwide who use smokeless tobacco products, most of whom live in low-[income] and middle-income countries where health systems are less well-resourced to diagnose and treat noncommunicable diseases. High-risk oral tobacco products such as betel quid, paan or gutkha contain relatively high levels of carcinogenic and toxic compounds and increase the risk of oral, esophageal and pancreatic cancers. In contrast, nicotine pouches have been found to have a similar risk profile to nicotine replacement therapy.
“Nicotine pouches may not yet be as widely used as nicotine vapes, but the global market for these products is already worth $1.5 billion. This provides good evidence that tobacco users find these products acceptable and will switch to them. In comparison to some other safer nicotine product categories, nicotine pouches are low cost and have minimal start-up and on-costs for consumers, meaning they offer significant hope to many low-[income] and middle-income countries where high-risk oral tobacco use is prevalent.”