 The ninth Conference of the Parties (COP9) to the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) will operate under conditions of secrecy comparable to those of the U.N. Security Council, according to a new report by the Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction (GSTHR) titled, Fighting the Last War: The WHO and International Tobacco Control.
The ninth Conference of the Parties (COP9) to the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) will operate under conditions of secrecy comparable to those of the U.N. Security Council, according to a new report by the Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction (GSTHR) titled, Fighting the Last War: The WHO and International Tobacco Control.
The public and media are banned from attending all but one largely ceremonial opening plenary, yet millions will be affected by the decisions taken at COP9, which is scheduled to take place virtually Nov. 8–13.
The report contends that current implementation of the FCTC is a global public health failure. In force since 2005, when there were 1.1 billion smokers around the world, the FCTC set out the principles of global tobacco control—to reduce the death and disease caused by smoking. In 2021, however, there are still 1.1 billion smokers worldwide and 8 million smoking-related deaths each year. What’s more, the number of smokers is predicted to rise, and the number of smoking-related deaths is set to top 1 billion this century.
Change is urgently needed, and harm reduction for tobacco offers the opportunity for that change, according to the GSTHR.
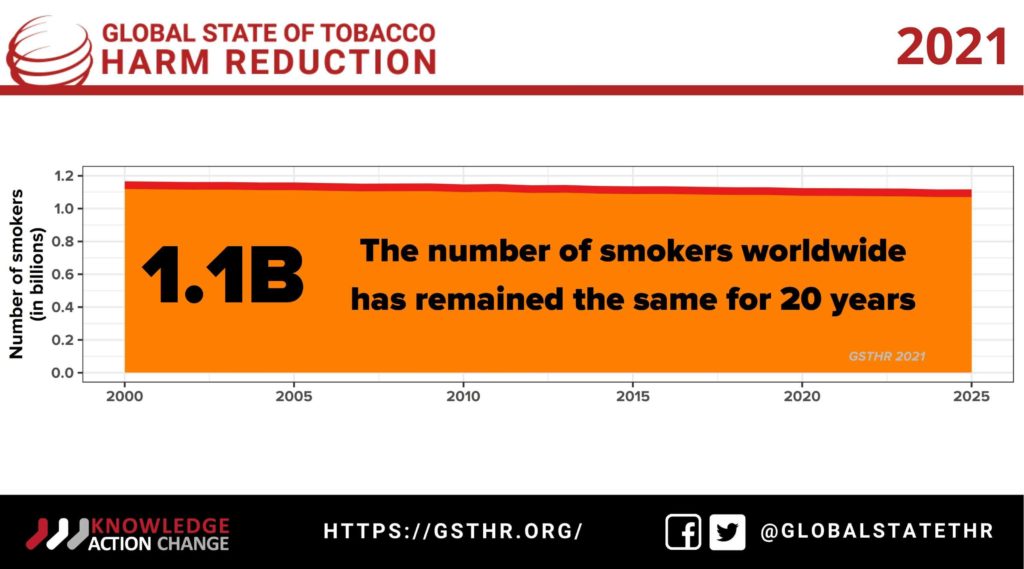
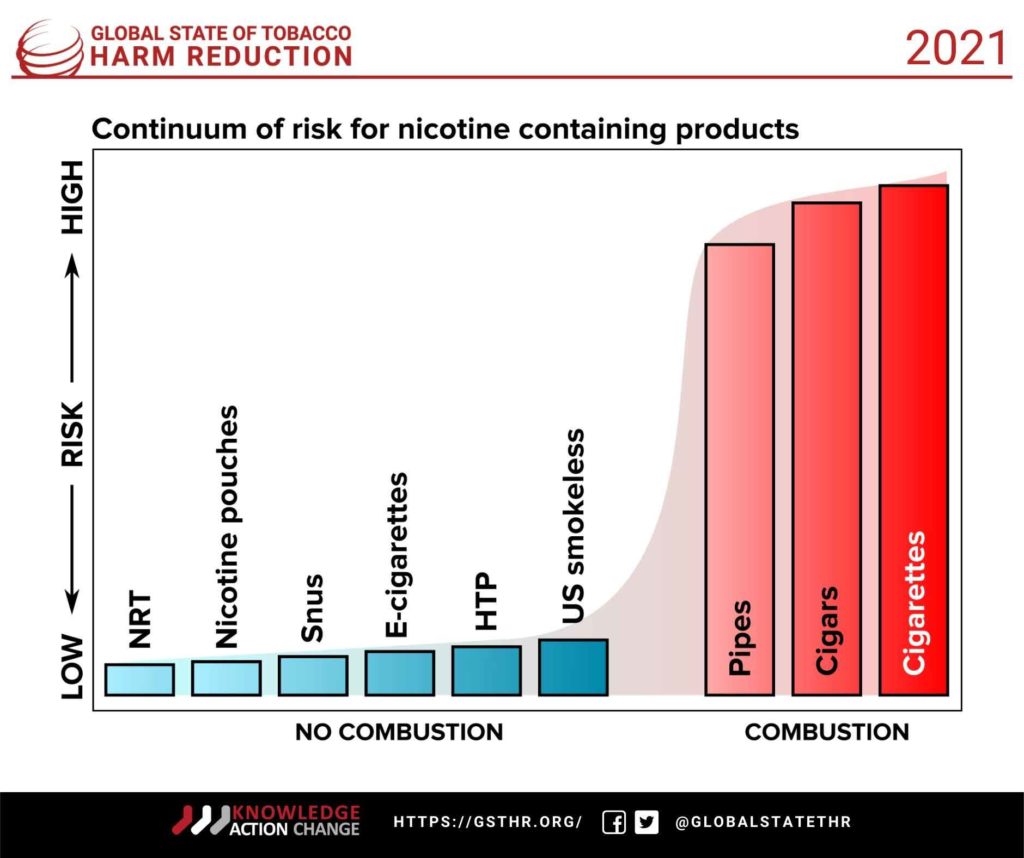
Fighting the Last War notes that while tobacco control policy has remained frozen in time, innovative noncombustible nicotine technology and supporting evidence have moved forward. Vaping devices, snus, nicotine pouches and heated-tobacco products are significantly safer than cigarettes as they deliver nicotine without combustion, according to the report’s authors. This, they argue, enables people who cannot or do not want to stop using nicotine to quit deadly smoking and switch to less risky products.
“Just as delegates at COP26 will be discussing the world’s urgent need to stop fossil fuel combustion, the technology is now in place to ensure the end of the age of combustion for tobacco as well,” the GSTHR wrote in a press note. “A number of Parties to the FCTC, such as the United Kingdom and New Zealand, have successfully introduced tobacco harm reduction policies alongside their tobacco control regimes and have seen marked decreases in smoking rates.”
When given accurate information about comparative risk, many smokers switch, the organization notes. Worldwide, the GSTHR estimated in 2020 that 98 million people worldwide were using safer nicotine products.
The authors also point out that the concept of harm reduction is embedded in the WHO response to drug use and HIV/AIDS. It is explicitly named as the third pillar of tobacco control alongside demand and supply reduction in the FCTC. Yet the WHO has remained implacably opposed to harm reduction for tobacco and is increasingly viewed as having overseen a “mission creep,” which now sees international tobacco control setting its sights on prohibition for nicotine in all its forms.
“There are concerning signs in published agenda and briefing papers that the FCTC secretariat and leadership continue to urge Parties against increasing access to, or even to prohibit, safer nicotine products,” the GSTHR wrote.
Fighting the Last War considers the motivations—ideological, financial and historical—that have led to many global tobacco control practitioners becoming so hostile to what others see as the greatest potential public health advance in decades.
The report argues that Parties to the FCTC need to seize back control of the COP meetings from the FCTC secretariat, which it says has become overly influential with little oversight. FCTC Parties should press for more evidence-based discussions, calling upon the widest breadth of scientific, clinical and epidemiological expertise on safer nicotine products and tobacco harm reduction, according to the authors. “This should include evidence from Parties that have implemented harm reduction policies, those involved in manufacturing safer nicotine products and the lived experience of consumers,” they wrote. “The establishment of a working group on tobacco harm reduction would offer a pragmatic route to move the FCTC toward a tobacco control regime fit for purpose in the 21st century.”
“As global leaders prepare to make important pledges on climate change under the glare of the media spotlight at COP26, we urge them to demand more from their delegations inside the closed and unscrutinized rooms of COP9,” says Gerry Stimson, director of Knowledge-Action-Change and emeritus professor at Imperial College London. “Every day, more than one billion smokers are being failed by the international tobacco control regime. The age of combustion—for tobacco as for fossil fuels—must end.
“Tobacco harm reduction offers new routes out for adult smokers. GSTHR estimates suggest that 98 million of them have already switched. At COP9, government delegations must seize back control and prevent the slide into outright nicotine prohibition that would see many return to smoking and many millions more never succeed in quitting.”
“The fight to reduce eight million smoking-related deaths a year is now being actively undermined by the WHO and the international tobacco control establishment,” said report author Harry Shapiro. “Together, they are fighting the last war against the tobacco industry—to direct attention away from the evidence that safer nicotine products can make a significant contribution to reducing that death toll.”
“If those who dominate the global tobacco control discourse were truly committed to public health imperatives, harm reduction principles and policies would be front and center,” said Ethan Nadelmann, founder of the Drug Policy Alliance. “This valuable report exposes the ways in which international institutions have turned their backs on scientific evidence and the human and political rights of hundreds of millions of people whose lives might be saved by safer nicotine products.”
“Fighting the Last War provides an insight into the dark arts of the WHO that many would find breathtaking and incomprehensible,” said Jeannie Cameron from JCIC Consulting. “It shows a concerning difference between the world’s preparations for COP26 on climate change and COP9 on tobacco. Governments need to stand up at COP9 to support tobacco harm reduction against the outdated views of the WHO.”

The fight to reduce eight million smoking-related deaths a year is now being actively undermined by the WHO and the international tobacco control establishment. Together, they are fighting the last war against the tobacco industry—to direct attention away from the evidence that safer nicotine products can make a significant contribution to reducing that death toll.”
Harry Shapiro, author, ‘Fighting the Last War’
“The challenge for lower and middle-income countries while fighting the last war and promoting real tobacco control is about two major issues,” said Nataliia Toropova from Healthy Initiatives. “Firstly, the current provisions of the WHO FCTC have not been properly implemented due to stretched government resources. Thus, smoking cessation programs are nonexistent, and adult smokers feel hopelessly stuck while making their numerous unsuccessful attempts to quit with no medical help or guidance provided. Secondly, the lack of a comprehensive harm reduction strategy is aggravated by a massive misinformation campaign about harm reduction products and a declared war on nicotine. Unless these two issues get tackled, unless the powerful voice of doctors becomes loud and gets heard, unless education and awareness building campaigns take place, no changes will occur, and this last war will be lost.”





















