European smokers bought more than 35 billion illicit cigarettes in 2023, accounting for 8.3 percent of total EU cigarette consumption, according to a KPMG study commissioned by Philip Morris Products.
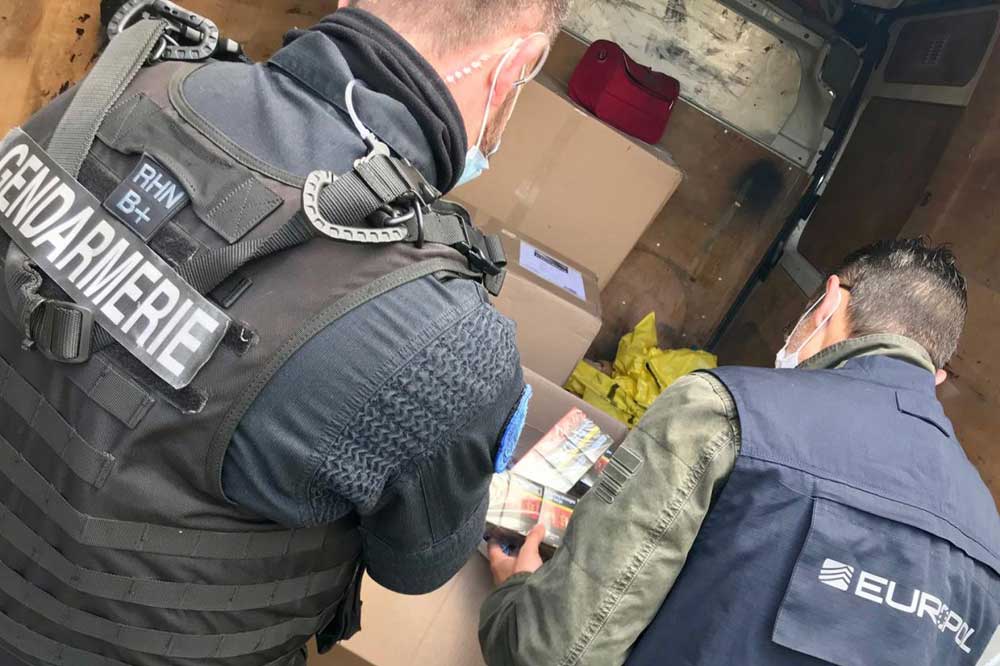
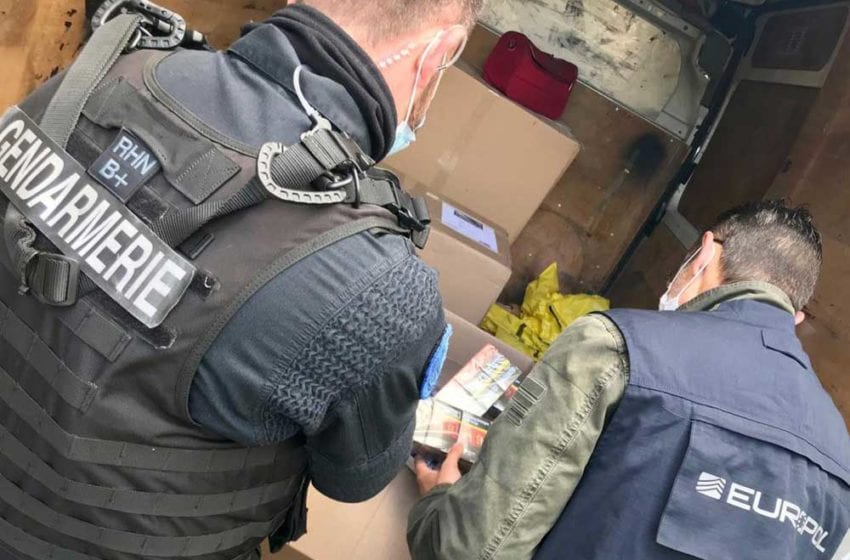
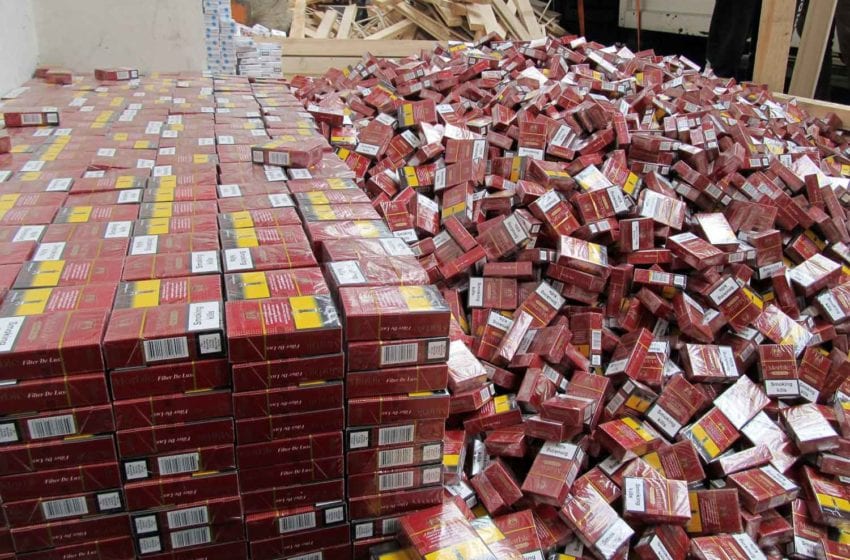
Counterfeit cigarettes remain one of the main sources of illicit tobacco consumption in the region, with 12.7 billion (36 percent) cigarettes consumed, as criminal networks increasingly target higher-taxed and higher-priced markets. Overall, governments in the EU lost an estimated €11.6 billion (12.82 billion) in tax revenue, up from €11.3 billion in 2022. France is still leading the ranking as the country with the largest illicit consumption in all of Europe, with 16.8 billion illicit cigarettes and an estimated €7.3 billion in tax revenues lost.
“We are witnessing an evolution of organized crime groups in Europe, as they are increasingly locating production facilities nearer Western European countries,” said PMI Senior Vice President of External Affairs Christos Harpantidis in a statement.
“We consider this phenomenon to be a direct consequence of failed policy approaches that have not done enough to curb illicit trade and reduce smoking prevalence, and it is putting consumers, governments, legitimate businesses, and society alike at risk.”


We consider this phenomenon to be a direct consequence of failed policy approaches that have not done enough to curb illicit trade and reduce smoking prevalence, and it is putting consumers, governments, legitimate businesses, and society alike at risk.
Christos Harpantidis, senior vice president, external affairs, PMI
Interviews with law enforcement agencies included in the KPMG report shed light onto transnational organized crime’s professionalization of their role in the supply chain of illicit cigarettes. According to information from law enforcement agencies, publicly available media articles, and PMI estimates, criminals have expanded the setup of illegal cigarette factories; in 2023 alone, law enforcement data shows that at least 113 clandestine cigarette manufacturing sites in 22 European countries were disrupted by regional and local authorities.
The steady increase of counterfeit cigarette consumption for the fourth consecutive year across Europe—mainly driven by the U.K. and Ukraine—is now coupled with the rise of all other illicit trade categories, including illicit whites and contraband. Combined with the continued recovery of cross-border legal volumes, after Covid-related travel restrictions ended in 2022, total non-domestic consumption across the 38 European countries in the study has also reached its highest level ever (15.5 percent), equal to more than one cigarette out of six.
Despite this scenario, KPMG revealed that in 26 European countries illicit consumption share was less than 10 percent of total consumption. Of these, 16 markets had an illicit consumption share of less than 5 percent. And in 25 of the 38 European countries included in the study, the share of illicit cigarette consumption was either stable or declining, compared to 2022.


We need to continue working together with law enforcement agencies and governments to ensure that illicit trade does not become an even larger problem across the EU.
Massimo Andolina, president, Europe region, PMI
“It’s truly encouraging to see a decrease in illicit consumption in countries like Italy, Poland, Romania, and Spain. We need to continue working together with law enforcement agencies and governments to ensure that illicit trade does not become an even larger problem across the EU,” stated Massimo Andolina, president, Europe region, PMI.
For the first time since its publication in 2006, the KPMG annual research study has broadened its scope and incorporated all Balkan countries. Now, the research covers 38 countries: the 27 EU member states, as well as Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Switzerland, Ukraine, and the U.K.
The Balkan region has shown lower presence of illicit cigarettes compared to some of the Western European countries, such as France or the U.K. Ukraine, on the other hand, remains the country with the second highest volume of illicit cigarettes consumed, at 8.4 billion.